L2BEAT Bridges is a work in progress. You might find incomplete research or inconsistent naming. Join our Discord to suggest improvements!
 Polygon PoS
Polygon PoS
About
Polygon PoS it the official bridge provided by the Polygon team to bridge assets from Ethereum to Polygon chain. The bridge is validated by Polygon validators and allows for asset as well as data movement between Polygon and Ethereum.
About
Polygon PoS it the official bridge provided by the Polygon team to bridge assets from Ethereum to Polygon chain. The bridge is validated by Polygon validators and allows for asset as well as data movement between Polygon and Ethereum.
Funds can be stolen if
- validators decide to mint more tokens than there are locked on Ethereum thus preventing some existing holders from being able to bring their funds back to Ethereum,
- validators submit a fraudulent checkpoint allowing themselves to withdraw all locked funds,
- destination token contract is maliciously upgraded,
- a contract receives a malicious code upgrade. There is no delay on code upgrades (CRITICAL),
- the source code of unverified contracts contains malicious code (CRITICAL).
Users can be censored if
Outbound transfers are externally verified, inbound require merkle proof
Validators on the Polygon network watch for events on Ethereum, and when they see that tokens have been locked they mint new tokens on Polygon. Around every 30 minutes validators submit new Polygon state checkpoints to the Ethereum smart contracts. To withdraw tokens, users need to present a merkle proof of a burn event that is verified against the checkpoints.
Users can be censored if validators on Polygon decide to not mint tokens after observing an event on Ethereum.
Funds can be stolen if validators decide to mint more tokens than there are locked on Ethereum thus preventing some existing holders from being able to bring their funds back to Ethereum.
Funds can be stolen if validators submit a fraudulent checkpoint allowing themselves to withdraw all locked funds.
Destination tokens are upgradeable
Tokens transferred end up as wrapped ERC20 proxies, some of them are upgradable. The contract is named UChildERC20Proxy.
Funds can be stolen if destination token contract is maliciously upgraded.
The system uses the following set of permissioned addresses:
This is a Gnosis Safe with 5 / 9 threshold. Can propose and execute code upgrades.
Those are the participants of the PolygonMultisig.
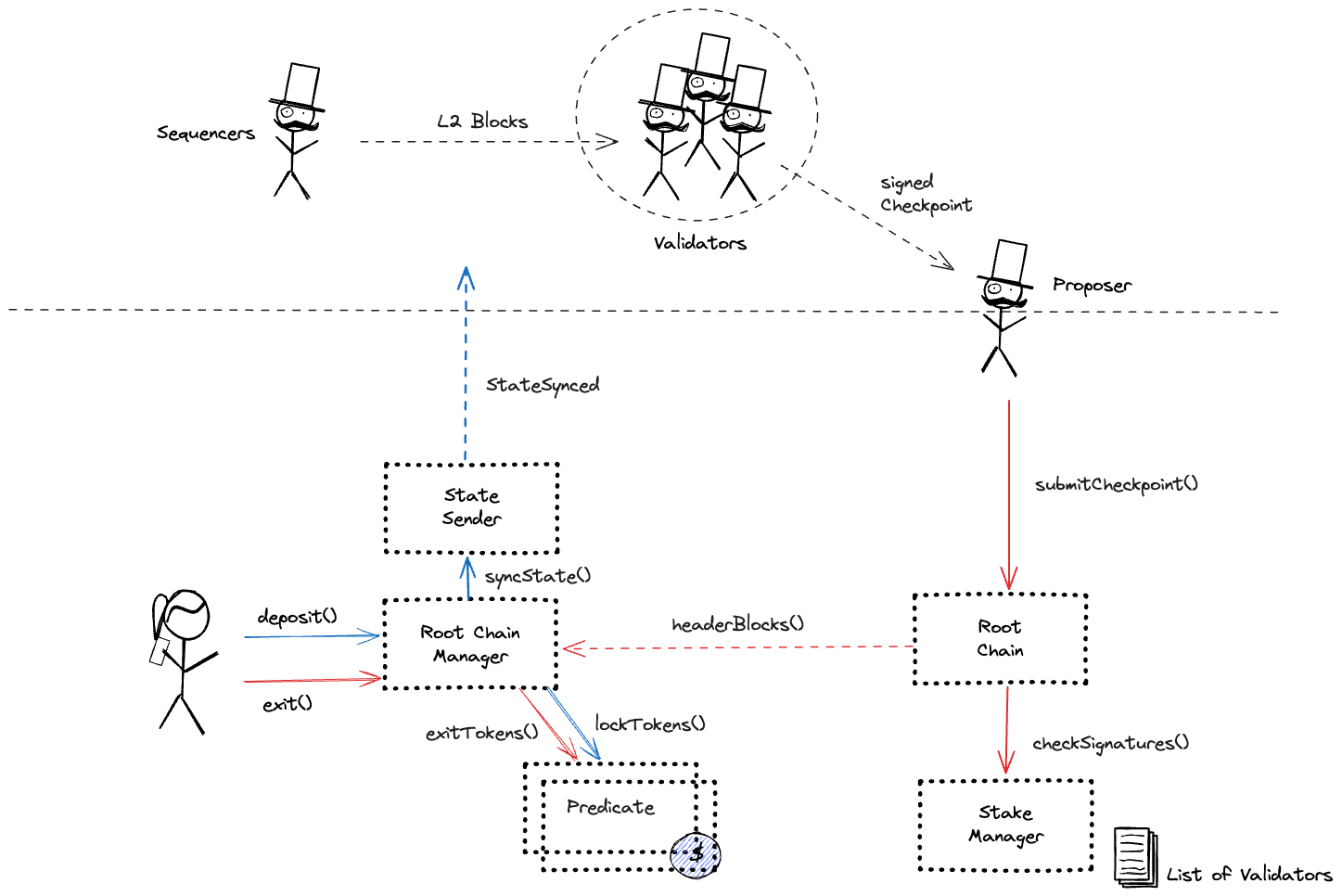
The system consists of the following smart contracts on the host chain (Ethereum):
Contract storing Polygon PoS chain checkpoints. Note that validity of these checkpoints is not verified, it is assumed to be valid if signed by 2/3 of the Polygon Validators.
Upgrade delay: No delay
Smart contract allowing whitelisted addresses to send messages to contracts on Polygon PoS chain.
Contains logging and getter functions about staking on Polygon.
A contract priviliged to slash validators in StakeManager via slash() method. The source code of this contract is not verified on Etherscan.
Upgrade delay: No delay
Maintains the addresses of the contracts used in the system.
Smart contract containing the logic for syncing the state of registered bridges to the other chain.
Contract to deposit and escrow ETH, ERC20 or ERC721 tokens. Currently only used for POL. This contract can store any token.
Upgrade delay: No delay
Contract used to initiate ERC20 token withdrawals. The function to handle Plasma proofs is empty, meaning exits cannot be challenged.
Contract used to initiate ERC721 token withdrawals. The function to handle Plasma proofs is empty, meaning exits cannot be challenged.
Contains events used by other contracts in the system.
Upgrade delay: No delay
NFTs used to represent a withdrawal in the withdrawal PriorityQueue (Only used for tokens initially deposited via DepositManager).
Contract enforcing delay on code upgrades. The current delay is 0s.
Main configuration contract to manage tokens, token types, escrows (predicates) for given token types. It also serves as an entry point for deposits and withdrawals effectively acting as a token router.
Upgrade delay: No delay
Main configuration contract to manage stakers and their voting power and validate checkpoint signatures.
Upgrade delay: No delay
Contract handling users’ withdrawal finalization for tokens escrowed in DepositManager.
Upgrade delay: No delay
Value Locked is calculated based on these smart contracts and tokens:
Upgrade delay: No delay
Upgrade delay: No delay
Upgrade delay: No delay
The current deployment carries some associated risks:
Funds can be stolen if a contract receives a malicious code upgrade. There is no delay on code upgrades (CRITICAL).
Funds can be stolen if the source code of unverified contracts contains malicious code (CRITICAL).
